We use machine learning technology to do auto-translation. Click "English" on top navigation bar to check Chinese version.
Improve cost visibility of Amazon ECS and Amazon Web Services Batch with Amazon Web Services Split Cost Allocation Data
Shubir Kapoor, Principal Product Manager, contributed to this blog
We’re excited to announce that the cost data for Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) tasks and Amazon Web Services Batch jobs is now available in the Amazon Web Services Cost and Usage Reports (CUR). With Amazon Web Services Split Cost Allocation Data, you can easily understand and optimize cost and usage of your containerized applications, and allocate application costs back to individual business entities based on how shared compute and memory resources are consumed by your containerized applications. Split Cost Allocation Data for ECS tasks and Amazon Web Services Batch jobs is available to customers in all Amazon Web Services commercial regions, excluding China regions, with no additional cost.
The challenges of monitoring and allocating container costs
As you modernize your applications with
In order to optimize and chargeback the cost of your containerized applications, you need more granular cost data, e.g., ECS task cost. Prior to the availability of Split Cost Allocation Data, you could access the cost of individual billable resources, such as EC2 instances, but didn’t have visibility into granular resources (such as ECS tasks and Amazon Web Services Batch jobs), since these container task-level resources were not used to compute your bill. You could potentially calculate the cost of the ECS resources with EC2 cost data and the usage data of ECS deployed on EC2 from your CUR report. Nevertheless, the process is complex and requires significant investment.
Get granular cost visibility of ECS tasks and Amazon Web Services Batch jobs with Split Cost Allocation Data
With Split Cost Allocation Data, you can now easily distribute your Amazon EC2 instance costs at the ECS task level, based on the actual consumption of the vCPU and memory utilized by your ECS tasks and your Amazon Web Services Batch jobs. The granular cost information at the container task level lets you analyze the cost efficiency of your containerized applications and simplifies the chargeback process to your business entities.
After Split Cost Allocation Data is enabled, it will scan for all of your ECS tasks or Amazon Web Services Batch jobs across your Consolidated Billing family and ingest usage telemetry data (actual and reserved CPU and memory) for your ECS resources and compute new ECS task-level metrics, e.g., split cost, unused cost, actual usage, and reserved usage, including net cost metrics after discounts. If you tag ECS resources or Amazon Web Services Batch jobs for billing purposes (see
Get started with Split Cost Allocation Data
To enable “Split cost allocation data”, you need to complete a simple two-step opt-in process. First, as a payer account owner, you need to opt-in “Split cost allocation data” from your Amazon Web Services Cost Management/Amazon Web Services Cost Explorer preference page. Then, you will enable “Split cost allocation data” for a new or existing CUR report from the Cost and Usage Reporting preference page in the Amazon Web Services Billing console. Once enabled, the report will automatically scan for ECS tasks for the entire Consolidated Billing family (all clusters belonging to member accounts across all regions) and start preparing the granular cost data for the current month. In 24 hours, your CUR report will be ready with the new ECS container task level metrics.
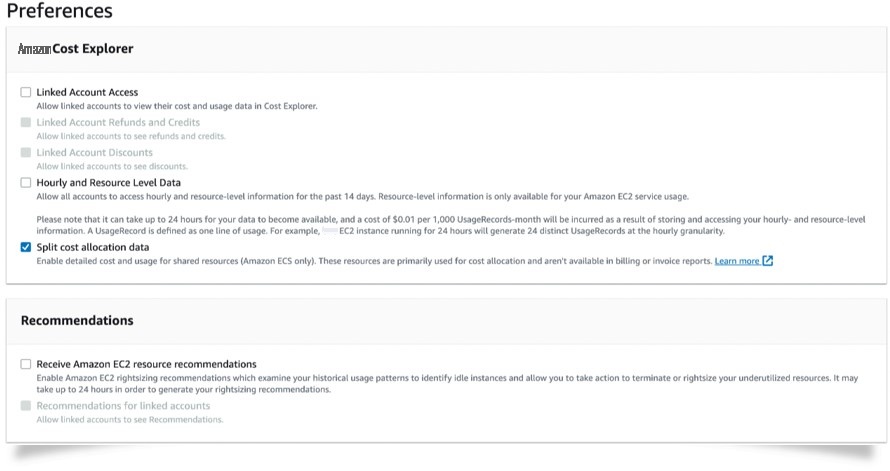
Figure 1. Enable “Split cost allocation data” from Cost Explorer preferences

Figure 2. Configure Cost and Usage Report (CUR) for “Split cost allocation data”
How it works
To help you understand how the cost model works, we’ll start by explaining a few key terms and calculation logic. Split Cost Allocation Data for ECS collects the reserved and actual usage data of compute and memory resources for each EC2 instance associated with an ECS cluster. It then calculates the allocated CPU and memory data for each ECS task based on the greater value between the reserved amount and the used amount.
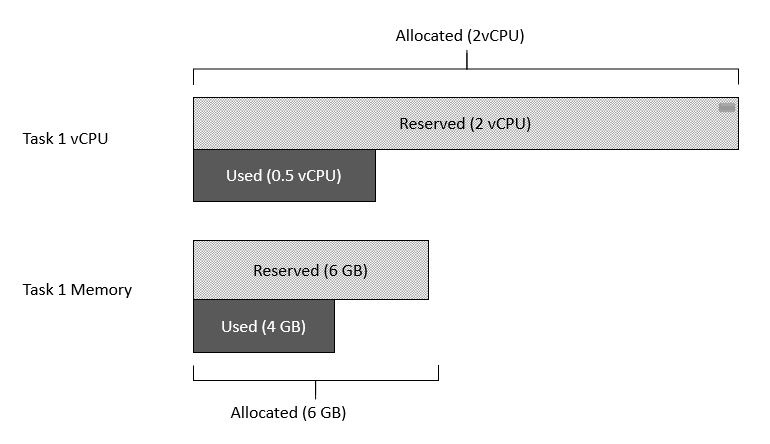
Figure 3. Allocated resources as the greater of reserved and actual utilization
Since multiple ECS tasks can run on a single EC2 instance, Split Cost Allocation Data for ECS computes the allocated CPU and memory for all tasks on the instance. It then computes a split-usage-ratio, the percentage of vCPU or memory allocated to each ECS task compared to the overall CPU or memory available on the EC2 instance. It also identifies the unused capacity left on the instance.
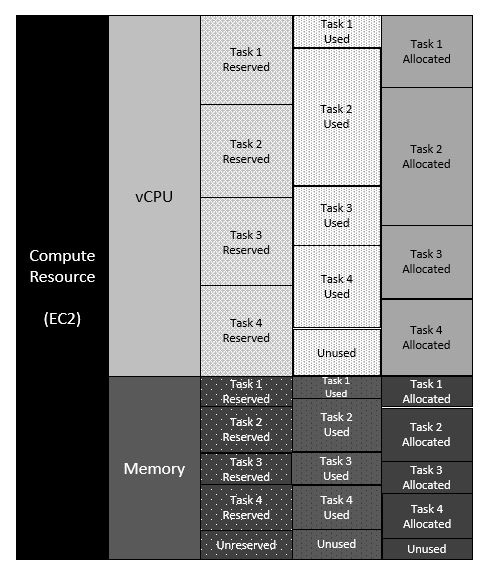
Figure 4. Resources allocated to multiple ECS tasks
When sharing the cost of the EC2 instance among all the ECS tasks, Split Cost Allocation Data totals the split cost and then proportionally redistributes the unused cost according to instance utilization by task.
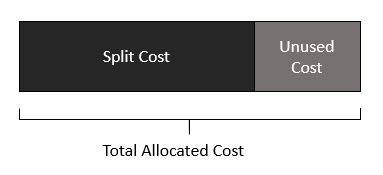
Figure 5. Total allocated cost equals split cost plus proportionally redistributed unused cost
Example: EC2 cost allocation across multiple ECS tasks
Now, let’s plug in some numbers and show how an EC2 instance cost is allocated across multiple ECS tasks.
Below you can see an ECS cluster run on a single node of m7g.2xlarge EC2 instance with 8 vCPU and 32GB RAM. The cluster is operating 4 ECS tasks across 2 ECS services. We will use the on-demand pricing for m7g.2xlarge for demonstration purposes. Split Cost Allocation Data uses relative unit weights for CPU and memory based on a 9:1 ratio. This is derived from average relative price of vCPU to memory based on Fargate pricing. Using these weights, it computes the cost per vCPU-Hour and cost per GB-Hour as $0.029 and $0.003, respectively.
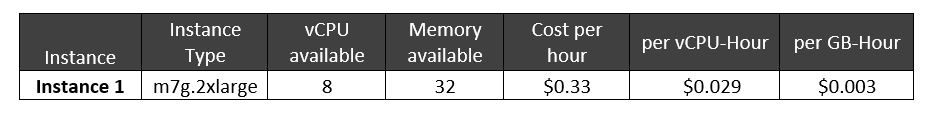
Table 1. m7g.2xlarge EC2 instance
The vCPU and memory reservation and actual usage across the 4 ECS tasks are listed in the table below. Task 2 used more CPU and memory than what was reserved because it didn’t configure a limit. As mentioned earlier, Split Cost Allocation Data computes allocated vCPU and memory based on the greater value between the reserved and actual usage. In this example, we don’t have any unused vCPU, but there is 2GB of unallocated memory.
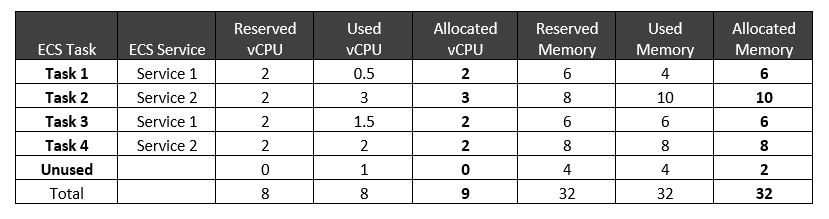
Table 2. Reserved, used, and allocated data for the ECS cluster
Split Cost Allocation Data computes a split-usage ratio as the percentage of CPU or memory allocated by the ECS task compared to the overall CPU or memory available on the EC2 instance. It also computes an unused ratio as the percentage of CPU or memory allocated by the ECS task compared to the overall CPU or memory allocated on the EC2 instance (that is, not factoring in the unallocated CPU or memory on the instance). For instance, there is 2GB of unallocated memory on the instance, which is 0.063 of the total instance memory. Therefore, the total unused memory ratio for Task 1 is 0.188 / (1-0.063) = 0.200.
The task-level split costs are calculated based on split-usage ratios multiplied by the cost per vCPU-Hour and cost per GB-Hour. If there is unused resource, in this case unused memory capacity of 2GB, the unused instance cost ($0.006) is proportionally distributed to each task based on the unused ratio computed for each task. The total allocated cost for each task will be the total of the split cost and proportionally redistributed unused cost. Once the EC2 cost is available at the task level, you can calculate the aggregate service-level costs. In this example, the total allocated cost for ECS service 1 and ECS service 2 are $0.142 and $0.188, respectively. You can also aggregate the costs using tags or Cost Categories that were added to the ECS tasks, allowing you to compute the cost by your desired business entity level.
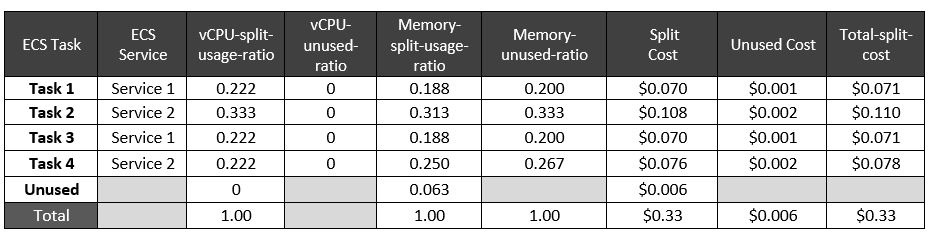
Table 3 Allocated cost data at the ECS task level
What are the new Cost and Usage Report columns?
As Split Cost Allocation Data computes ECS task-level metrics, you will see the new columns in your CUR reports. For instance, “SplitUsage” stands for the usage for vCPU or memory allocated for the specified time period to the Amazon ECS task. You can view this user guide for a complete list of the new CUR columns and their definitions.
To wrap up with our example, below is a demo CUR report. You can see how data will be displayed in the new CUR columns.
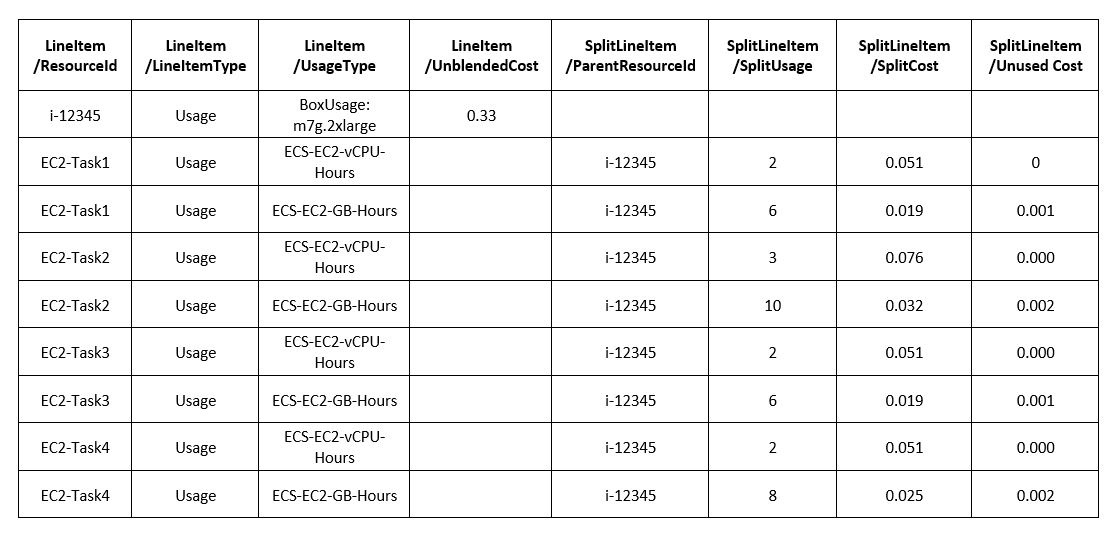
Table 4. Sample Cost & Usage Report data
Conclusion
The visibility of cost data at the ECS container-task level provides insights to improve efficiency and cost optimization.
The mentioned AWS GenAI Services service names relating to generative AI are only available or previewed in the Global Regions. Amazon Web Services China promotes AWS GenAI Services relating to generative AI solely for China-to-global business purposes and/or advanced technology introduction.