我们使用机器学习技术将英文博客翻译为简体中文。您可以点击导航栏中的“中文(简体)”切换到英文版本。
利用 亚马逊云科技 云运营服务提高云端可见性和监管 — 第 1 部分
许多客户正在
这篇由两部分组成的文章提供了基础工具,可帮助您集中和自动化操作,并通过
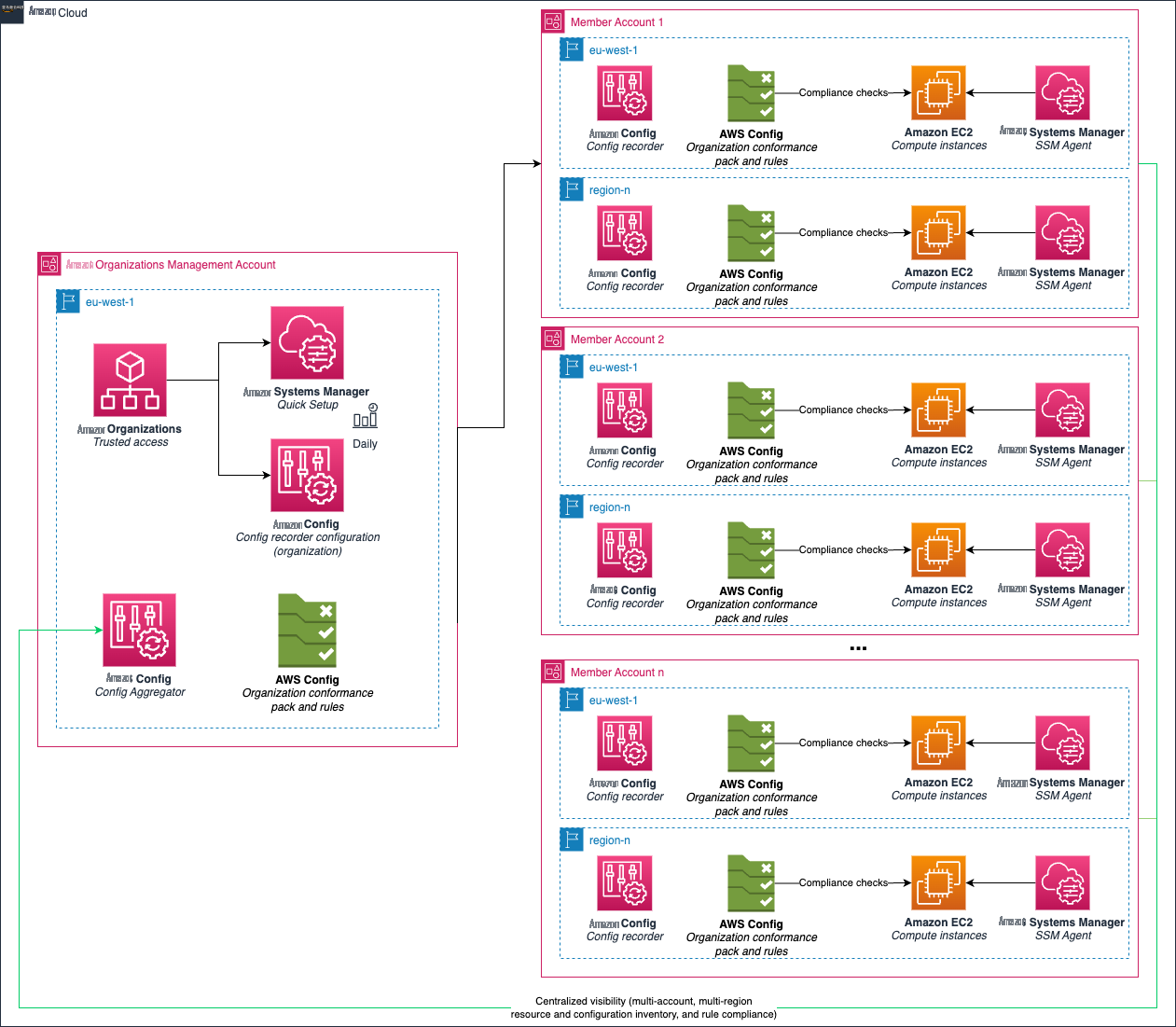
使用 亚马逊云科技 Organizations、亚马逊云科技 Systems Manager 和 亚马逊云科技 Config 进行基础跨账户监管的架构图。
先决条件
- 您已经有一个由 亚马逊云科技 Organizations 管理的多账户架构。
-
亚马逊云科技 O
rganization s 已启用 。亚马逊云科技 Config、亚马逊云科技 Systems Manager 和 AWS Backup 的可信访问权限 -
您熟悉使用
亚马逊云科技 Systems Manager 管理亚马逊弹性云计算(亚马逊 EC2)实例 和亚马逊云科技 Systems Manager 代理(SSM 代理) 。
解决方案概述
集中化治理和配置管理
以下步骤是大规模运营和治理的基础,也是集中化工具和自动化任务的基础。
1 — 使用 亚马逊云科技 Systems Manager 在所有账户和地区 设置 亚马逊云科技 Config
亚马逊云科技 Config 允许您详细跟踪您的 亚马逊云科技 资源(及其配置的任何更改)。这支持许多运营用例,例如资源管理、审计和合规性、配置管理和安全分析。我们建议您按照以下
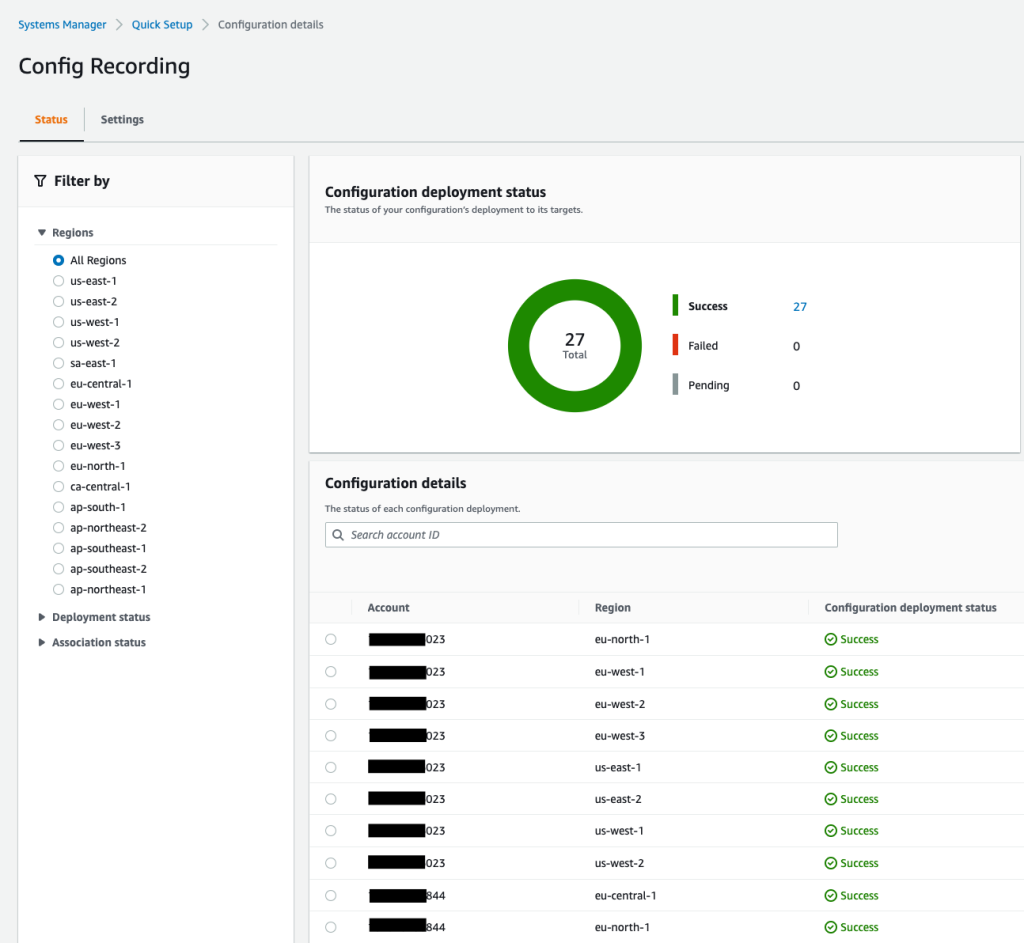
亚马逊云科技 Systems Manager 快速设置 — 配置记录在整个组织中部署配置
2 — 在组织层面 设置 亚马逊云科技 Config 聚合器
A
a. 集中资源列表
:具有搜索和筛选功能的跨多个账户区域的所有资源的集中清单,包括其配置数据。您可以在 “
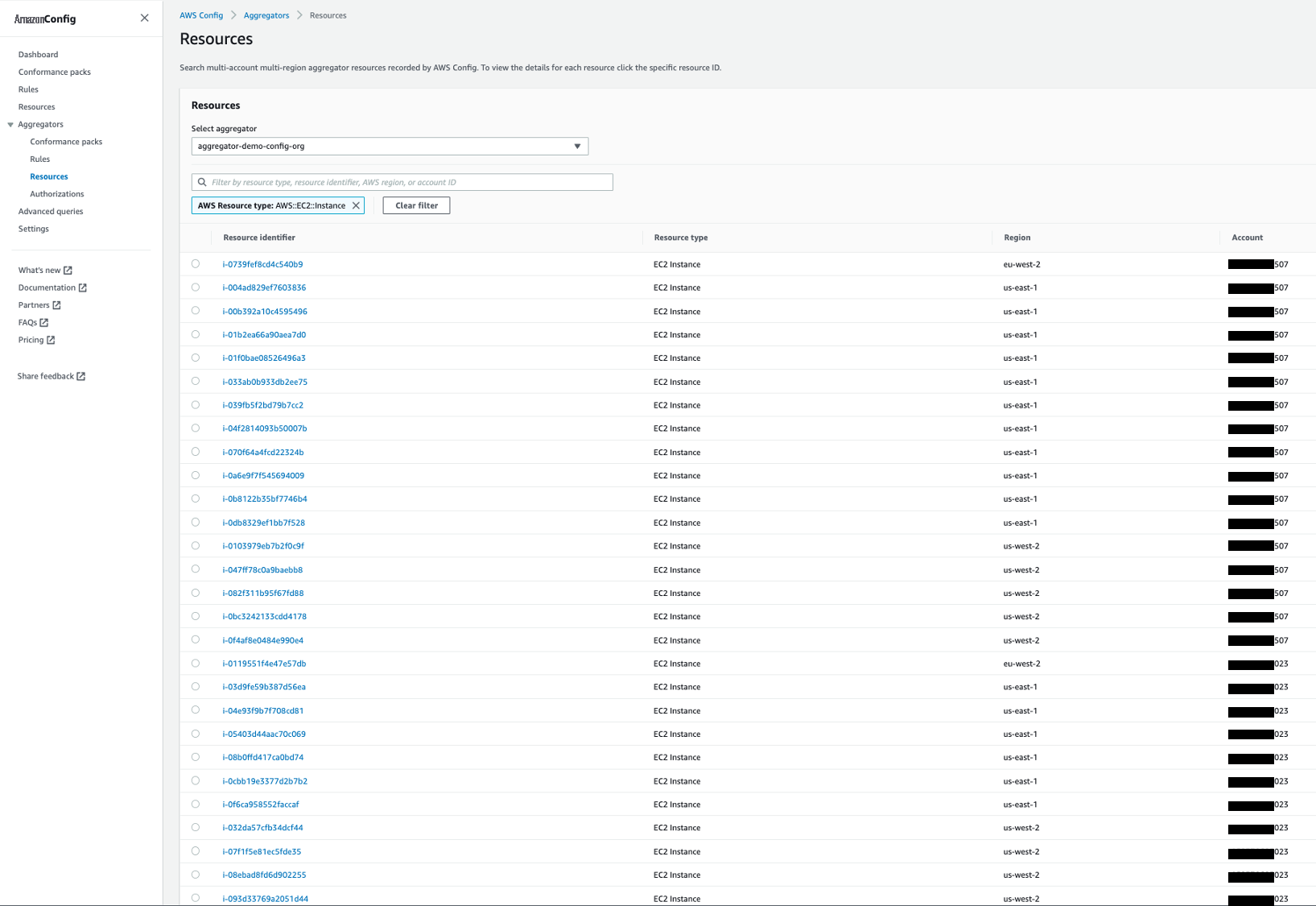
亚马逊云科技 Config 聚合器显示组织内所有 EC2 实例
b. 高级查询:
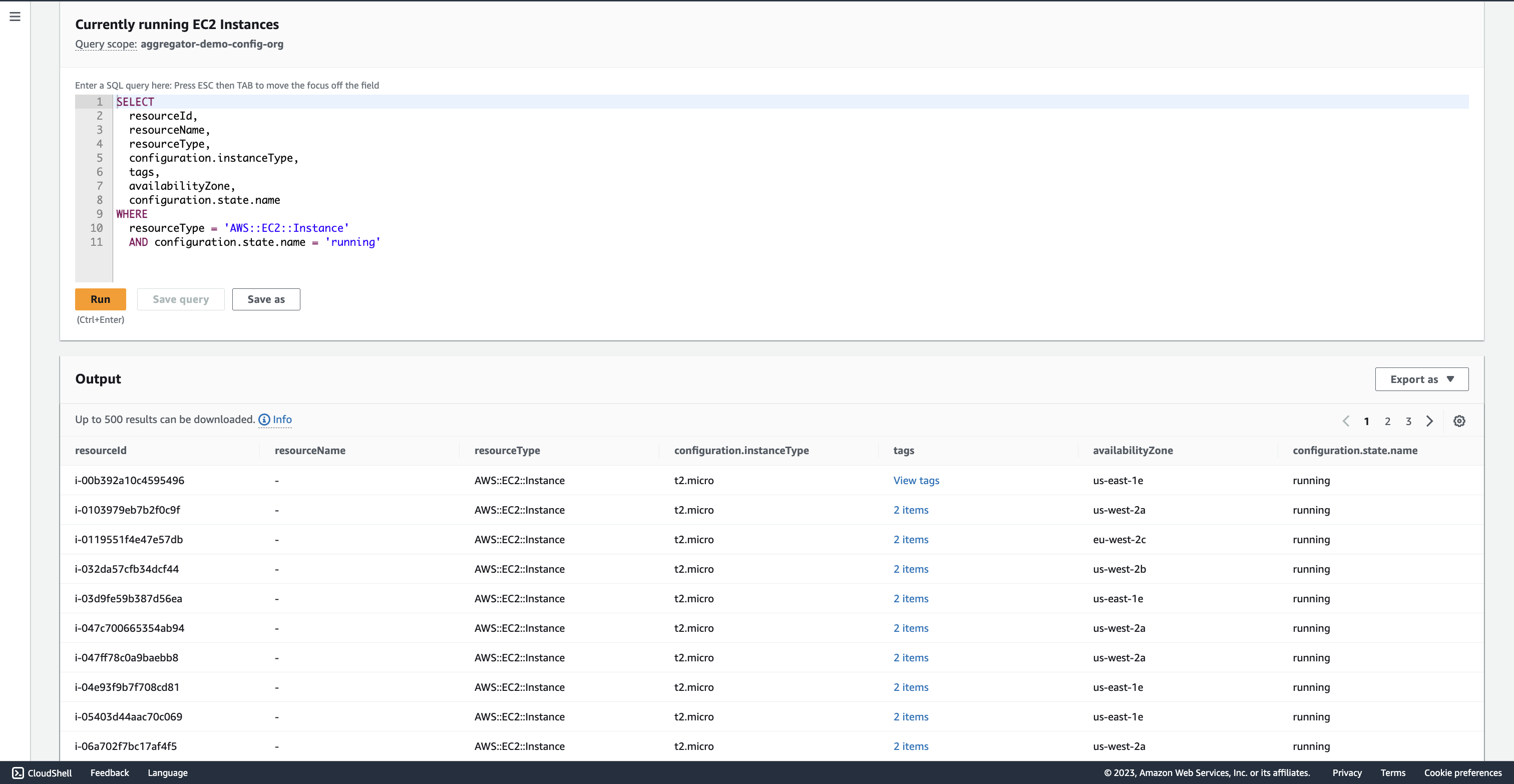
亚马逊云科技 Config 高级查询 — 针对组织级聚合器运行的示例查询(“描述当前正在运行的所有 EC2 实例”)
3 — 跨账户和区域 设置 亚马逊云科技 Config 规则
| Method | 亚马逊云科技 Service used | Technical considerations | Implementation |
| Console |
亚马逊云科技 Systems Manager (快速设置功能) |
-支持自定义一致性包(通过存储在 S3 中的 YAML 模板)。 -支持多区域部署 |
Follow these steps to
|
| 亚马逊云科技 CLI or API | 亚马逊云科技 Config |
-支持自定义一致性包(通过存储在 S3 中的 YAML 模板)。 -多区域部署不可用(API 调用因地区而异)。 |
请注意,跨账户部署规则和一致性包的 API 调用因地区而异。在组织层面,如果您想在其他区域部署规则,则需要将 API 调用的上下文更改为其他区域。 |
集中式合规报告和补救措施
:跨账户和区域的所有资源规则的合规状态将在
4 —
强制在所有 EC2 实例 上使用 SSM 代理
SSM 代理是 Amazon EC2 实例大规模管理和操作的 “心跳”。它定期提供有关实例的详细操作系统级信息,并通过自动化为许多有用的
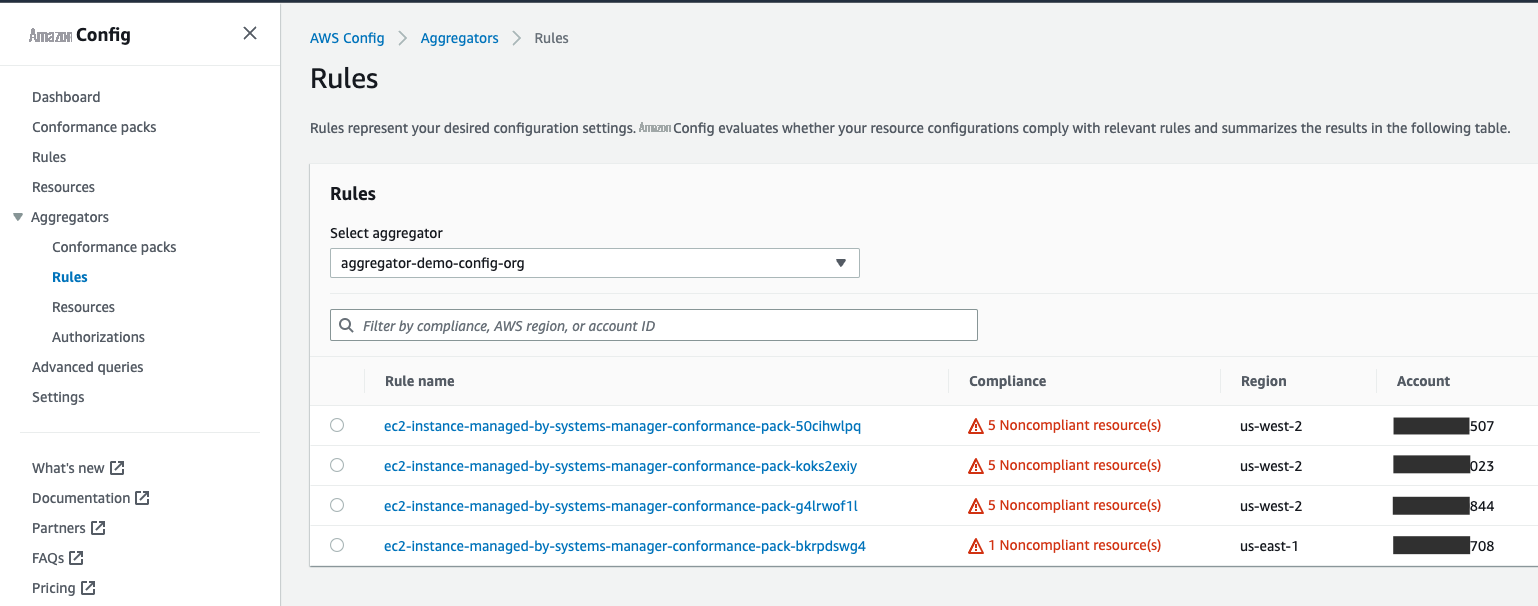
不合规的 亚马逊云科技 Config 规则的集中视图显示了跨区域的 EC2 实例未由 SSM 代理管理的账户。
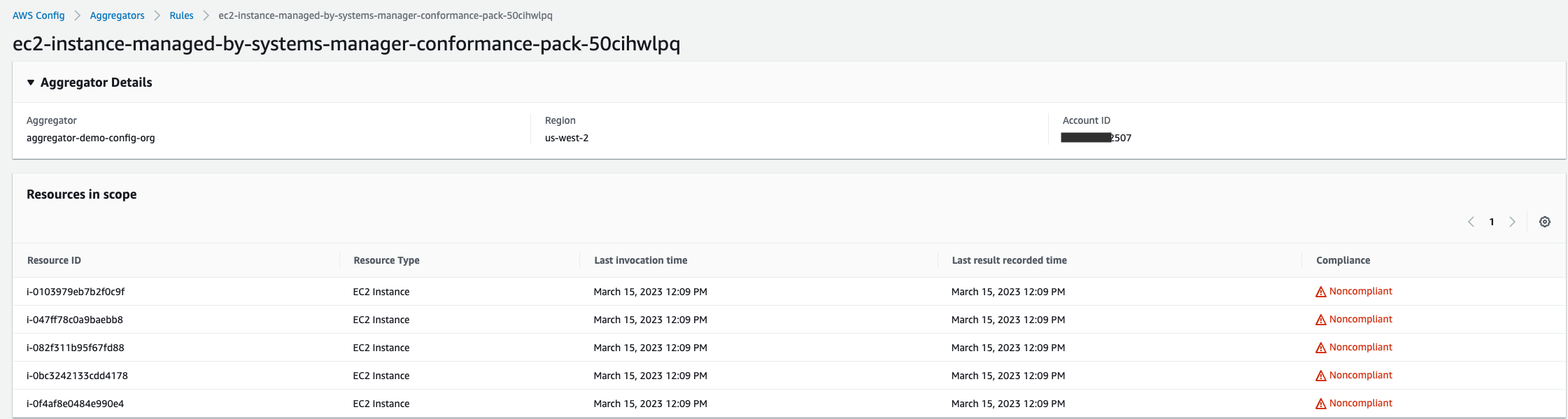 未由 SSM 代理管理的单个 EC2 实例的详细列表。
未由 SSM 代理管理的单个 EC2 实例的详细列表。
结论
在这篇博客文章中,我们向您展示了如何使用亚马逊云科技
在本系列 的
作者简介
*前述特定亚马逊云科技生成式人工智能相关的服务仅在亚马逊云科技海外区域可用,亚马逊云科技中国仅为帮助您发展海外业务和/或了解行业前沿技术选择推荐该服务。