我们使用机器学习技术将英文博客翻译为简体中文。您可以点击导航栏中的“中文(简体)”切换到英文版本。
实施自动方法来处理 亚马逊云科技 DMS 运营事件
亚马逊云科技 DMS 支持数据库的无缝迁移和复制,但有时在此过程中可能会出现错误。当这些错误可以恢复时,必须知道如何有效地恢复和完成任务,以确保数据完整性并最大限度地减少停机时间。在这篇文章中,我们探讨了恢复关系数据库目标任务的可恢复错误任务的过程。
概述
0078
和
007 9
特别重要,因为它们用于无缝恢复任务。
DMS-EVENT-0078
表示复制任务失败。
DMS-EVENT-0079
表示复制任务已停止。
您可以在 亚马逊云科技 DMS
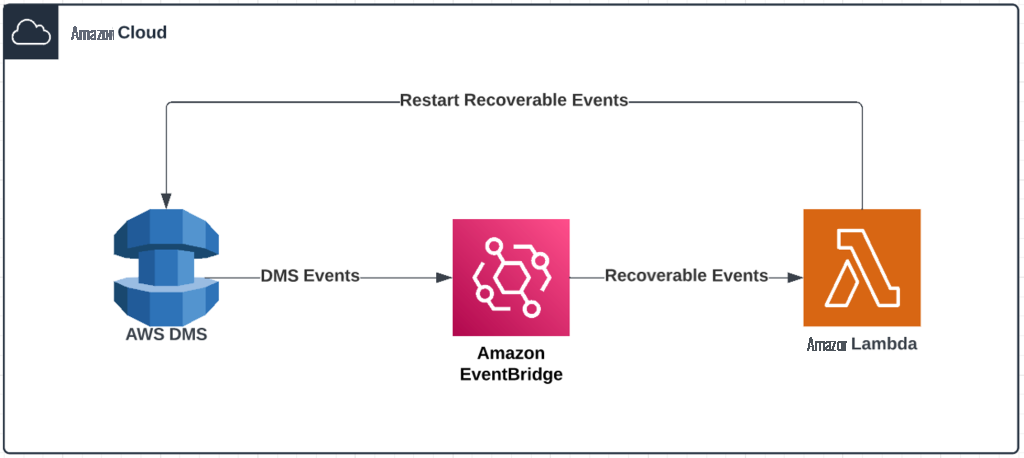
当 DMS 生成事件时,它会将其发送到
使用这种架构,该解决方案将自动恢复可恢复的任务。
先决条件
在本演练中,您必须完成以下先决条件:
- 您必须拥有一个活跃的 亚马逊云科技 账户,该账户将作为您所有基于云的活动的基础。
- 配置虚拟私有云 (VPC),因为 亚马逊云科技 DMS 在这个隔离的网络环境中运行以确保安全的数据传输。
- 对 DMS 概念和功能的基本了解将极大地增强您对服务的体验。
- 对 亚马逊云科技 Lambda 有基本了解,该服务可让您运行代码以响应事件并运行必要的停止或恢复任务命令,而无需管理服务器
部署
在本节中,我们将引导您了解如何部署此解决方案。要启动所提供的 CloudFormation 模板,请完成以下步骤:
- 使用中央账户登录控制台。
-
选择启动堆栈:

- 选择 “下一步”。
-
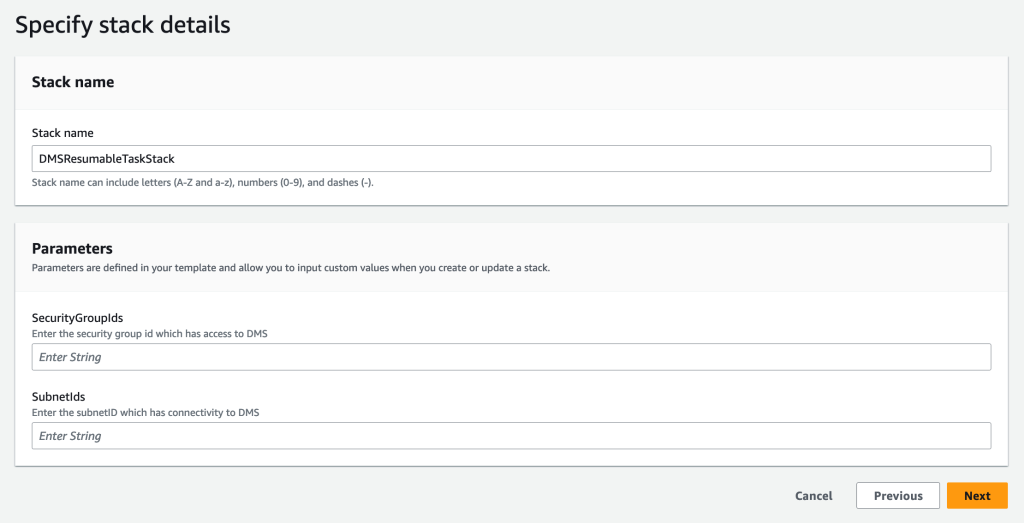
在堆栈名称中,输入一个名称。例如,
dmsResumableTaskStack。 -
为 亚马逊云科技 Lambda 函数提供安全组 ID 和子网 ID,该函数必须提供与 DMS API 的连接。
- 选择 “ 下一步 ” 。
- 输入要分配给堆栈的任何标签,然后选择 下一步 。
-
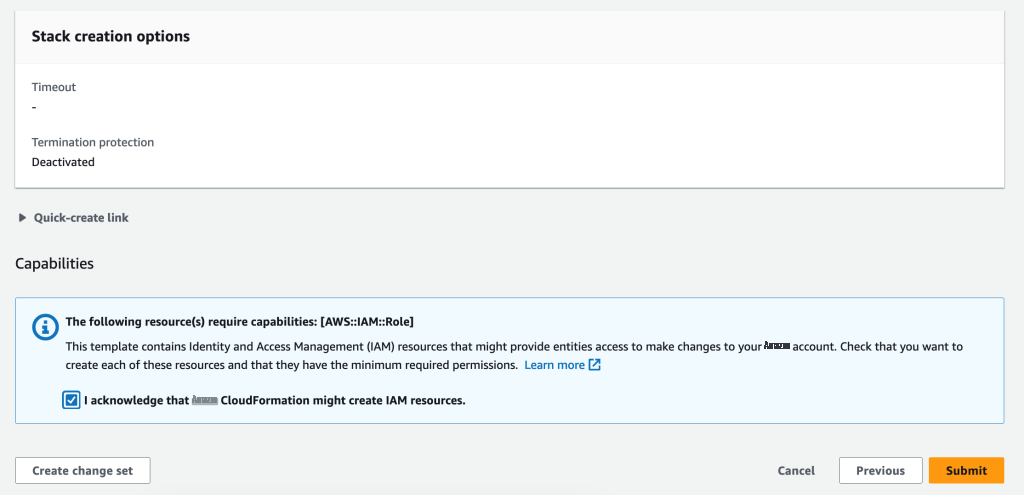
选中确认复选框并选择
提交
。
 堆栈大约需要 5 分钟才能完成。等到堆栈完成后再继续测试和验证。
堆栈大约需要 5 分钟才能完成。等到堆栈完成后再继续测试和验证。
注意
:随着 亚马逊云科技 Lambda 的执行
其他规则
EventBridge 接收事件,该事件是 亚马逊云科技 DMS 环境变化的指标,并应用规则将事件路由到通知机制。规则根据事件的结构(称为事件模式)将事件与通知机制进行匹配。你可以前往 EventBridge 添加额外的
eventId
来自动重启任务。更新 EventBridge 规则。
-
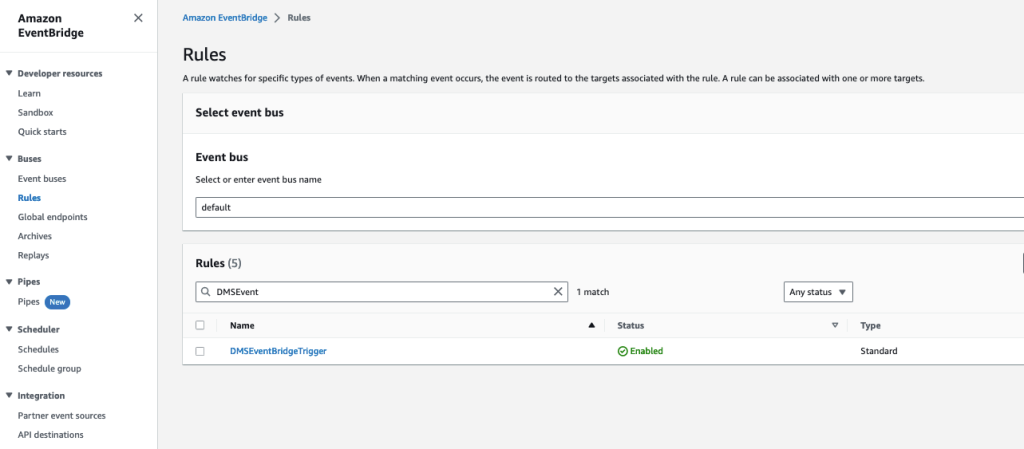
前往 Amazon EventBridge 并选择您在上一节中创建的 DMS 规则。
-
编辑事件规则, 根据您的要求添加其他
EventID,然后选择下一步。
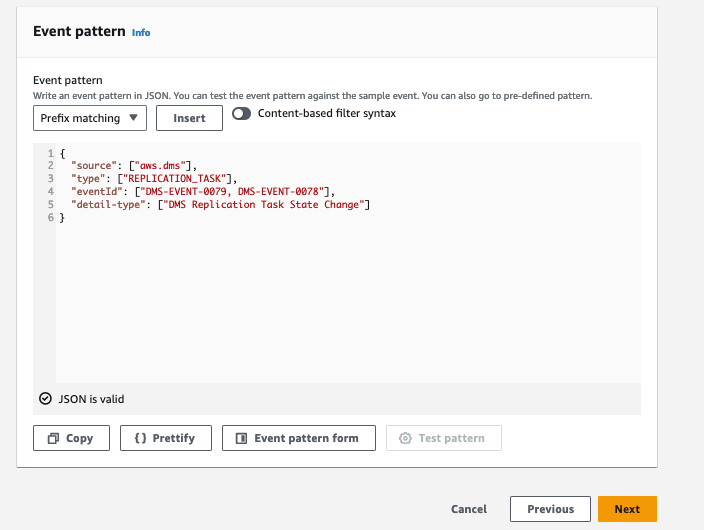
- 查看新添加的规则,然后选择更新规则。
注意: 通过将 DMS 操作事件纳入 EventBridge 规则来 更新 DMS 事件,从而启用 DMS 任务的自动重启。选择这些事件时务必谨慎,确保只有那些不需要干预的事件才包含在 EventBridge 规则中。
测试和验证
- 前往 DMS 控制台,在数据库迁移任务下选择迁移任务,然后选择 停止。
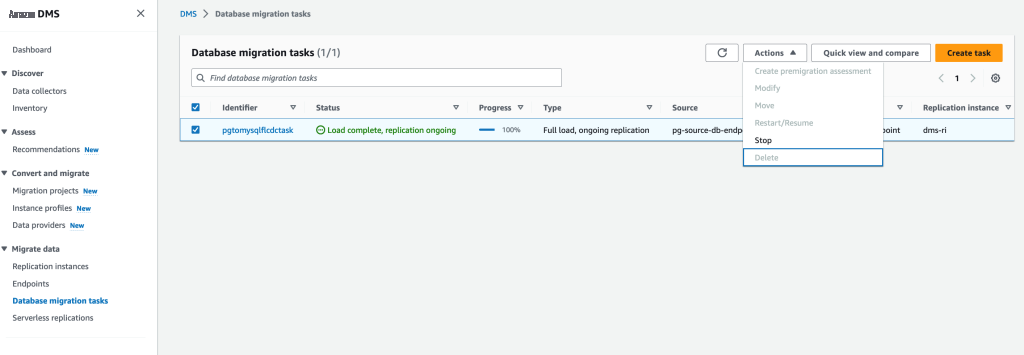
- 等待几分钟,这应该会触发 EventBridge 规则来调用 lambda,这将恢复任务。
-
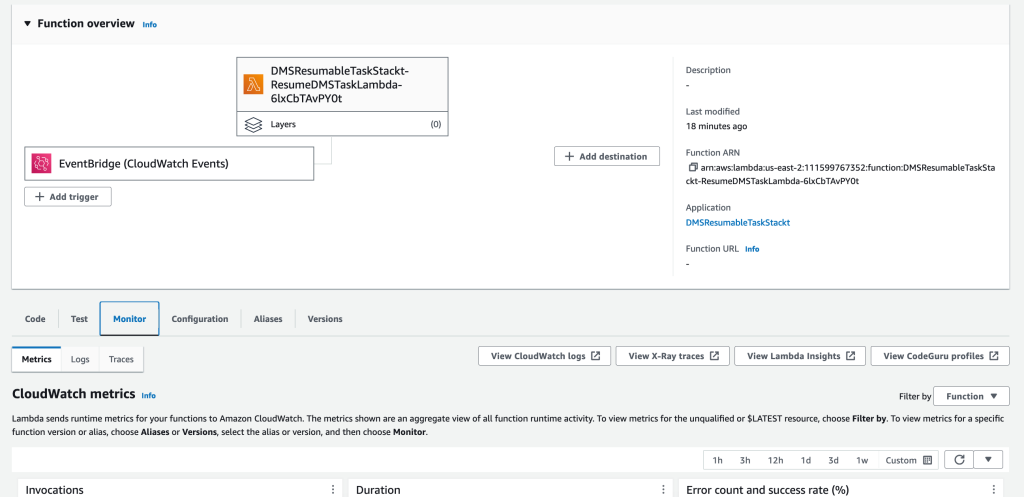
要进行故障排除,请前往 亚马逊云科技 Lambda 控制台,
选择 “StackName- ” Lambda 函数,然后选择 “查看
亚马逊 CloudWatchLogs” 并查找任何错误。
正在清理
为避免将来产生费用,请前往 亚马逊云科技 CloudFormation 控制台,选择堆栈并删除堆栈。
结论
在这篇文章中,我们使用 亚马逊云科技 Lambda 和亚马逊 EventBridge 来自动恢复 亚马逊云科技 DMS 中可恢复的错误任务的流程。通过设置 EventBridge 规则来捕获特定事件 ID,我们可以调用 Lambda 函数来分析和处理可恢复的错误,从而无需手动干预并确保更流畅的迁移体验。
如果您有任何问题或反馈,请发表评论。
作者简介
 费利克斯·戴维
是 亚马逊云科技 的高级技术客户经理。他与 亚马逊云科技 客户合作,帮助他们了解业务和技术需求,协调技术解决方案,并从 亚马逊云科技 中实现最大价值。
费利克斯·戴维
是 亚马逊云科技 的高级技术客户经理。他与 亚马逊云科技 客户合作,帮助他们了解业务和技术需求,协调技术解决方案,并从 亚马逊云科技 中实现最大价值。
 哈里什·班奈 是 A
WS 的高级技术客户经理。他与企业客户合作,提供有关 RDS、数据库迁移服务运营性能的技术援助,并共享数据库最佳实践。
哈里什·班奈 是 A
WS 的高级技术客户经理。他与企业客户合作,提供有关 RDS、数据库迁移服务运营性能的技术援助,并共享数据库最佳实践。
 Kanwar Bajwa
是 亚马逊云科技 的企业支持主管,他与客户合作以优化他们对 亚马逊云科技 服务的使用并实现其业务目标。
Kanwar Bajwa
是 亚马逊云科技 的企业支持主管,他与客户合作以优化他们对 亚马逊云科技 服务的使用并实现其业务目标。
*前述特定亚马逊云科技生成式人工智能相关的服务仅在亚马逊云科技海外区域可用,亚马逊云科技中国仅为帮助您发展海外业务和/或了解行业前沿技术选择推荐该服务。