我们使用机器学习技术将英文博客翻译为简体中文。您可以点击导航栏中的“中文(简体)”切换到英文版本。
检测和停止 亚马逊云科技 Lambda 函数中的递归循环
这篇文章由首席无服务器专家 TAM Puthran、高级无服务器专家解决方案架构师 Aneel Murari 和 亚马逊云科技 Lambda 高级产品经理 Shree Shrikhande 撰写。
这有助于降低因递归而意外调用 Lambda 函数所产生的成本。您可以通过
概述
您可以通过
现在,在超过 16 次调用后,Lambda 会检测到在支持的服务之间的递归循环中运行的函数。它向调用者返回 rec
ursiveInvocationException。
此功能不收取额外费用。对于异步调用,Lambda 会将事件发送到
以下是订单处理系统的示例。
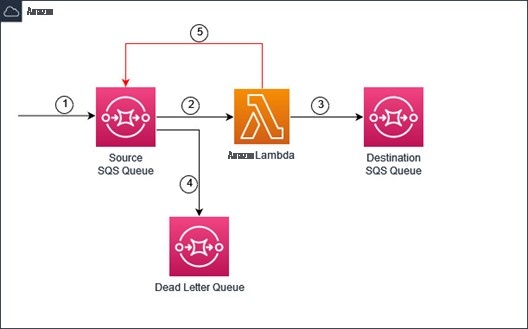
订单处理系统
- 新的订单信息消息被发送到源 SQS 队列。
- Lambda 使用 ESM 消耗来自源队列的消息。
-
Lambda 函数处理消息并使用 SQS SendMessage API 将更新的订单消息发送到目标 SQ S 队列。 - 源队列有一个死信队列 (DLQ),配置为处理任何失败或未处理的消息。
- 由于配置错误,Lambda 函数将消息发送到源 SQS 队列而不是目标队列。这会导致 Lambda 函数调用的递归循环。
要浏览此示例的示例代码,请参阅
在前面的示例中,在调用 16 次之后,Lambda 会向 ESM 抛出一个 recursiveInvocationException。
ESM 停止调用 Lambda 函数,一旦超过 ma
您会收到 亚马逊云科技 Health Dashboard 通知,其中包含对功能进行故障排除的步骤。
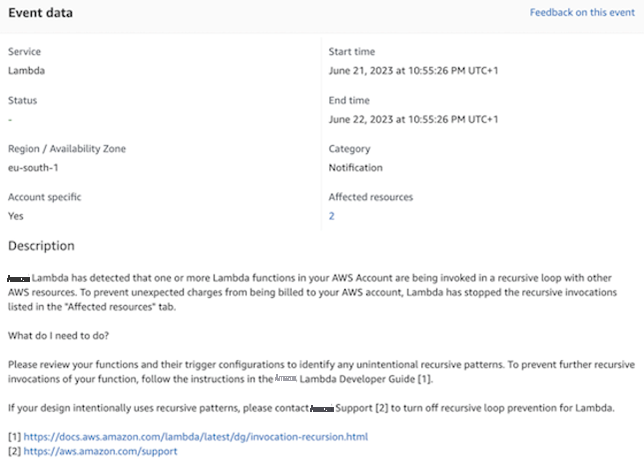
亚马逊云科技 Health 控制面板通知
您还会收到一封发送到该帐户中注册的电子邮件地址的电子邮件通知。

电子邮件通知
Lambda 会发出一个 rec ursiveInvocationsDroped CloudWatch 指标,你可以 在 CloudWatch 控制台中查看该指标。
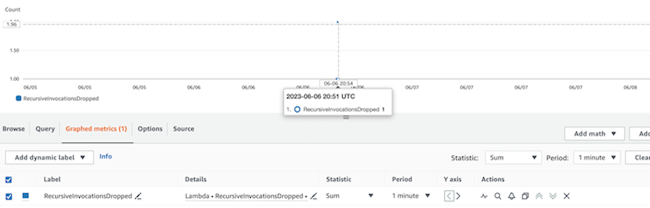
递归调用删除了 CloudWatch 指标
Lambda 是如何检测递归的?
要让 Lambda 检测递归循环,您的函数必须使用
Lambda 使用 名为 “Lineage” 的
血统标题的示例如下所示:
x-amzn-trace-id: root=1-645f7998-4b1e232810b0bb733dba2eab;parent=5be88d12eefc1fc0;Sampled=1;Lineage= 43e12f0f:5
43e12f0f 是资源的哈希值,在本例中为 Lambda 函数。 5 是使用相同事件调用此函数的次数。世系标头的哈希生成、编码和大小的逻辑将来可能会发生变化。您不应在此基础上设计任何应用程序功能。
使用 ESM 消费来自 SQS 的消息时,在超过
使用 SQS 时,您还可以将多条消息批处理成一个 Lambda 事件。当消息批量大小大于 1 时,Lambda 使用消息批次中的最大谱系值。如果值超过 16,它将删除整批数据。
递归检测在行动
您可以在
作为先决条件,你必须安装:
-
亚马逊云科技 命令行接口 (亚马逊云科技 CLI) -
亚马逊云科技 无服务器应用程序模型 (亚马逊云科技 SAM) (版本 1.81.1 或更高版本) -
Docker
要部署应用程序,请执行以下操作:
-
- 设置您的 亚马逊云科技 区域:
export REGION=<your AWS region>-
- 克隆 GitHub 存储库
git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/aws-lambda-recursion-detection-sample.git
cd aws-lambda-recursion-detection-sample-
-
使用 亚马逊云科技 SAM 构建资源并将其部署到您的 亚马逊云科技 账户。出现提示时,输入堆栈名称,例如
lambda-recursion。接受剩余的默认值。
-
使用 亚马逊云科技 SAM 构建资源并将其部署到您的 亚马逊云科技 账户。出现提示时,输入堆栈名称,例如
sam build –-use-container
sam deploy --guided --region $REGION
要测试应用程序,请执行以下操作:
-
- 将 SQS 队列的名称保存在本地环境变量中:
SOURCE_SQS_URL=$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks \ --region $REGION \ --stack-name lambda-recursion \ --query 'Stacks[0].Outputs[?OutputKey==`SourceSQSqueueURL`].OutputValue' --output text)- 向源 SQS 队列发布消息:
aws sqs send-message --queue-url $SOURCE_SQS_URL --message-body '{"orderId":"111","productName":"Bolt","orderStatus":"Submitted"}' --region $REGION这将调用 Lambda 函数,该函数将消息写回队列。
要验证 Lambda 是否已检测到递归,请执行以下操作:
-
导航到 CloudWatch 控制台。 在左侧面板的 “
指标” 下选择 “ 所有
指标
”,然后搜索 R
ecur
siveInvocationsDroped。
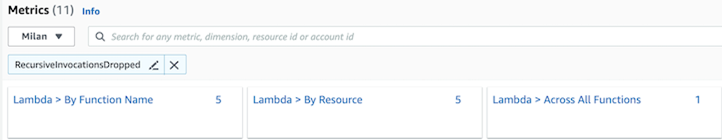
查找已删除的递归调用。
- 选择 Lambda > 按函数名称, 然后为您创建的函数 选择 RecursiveInvocat ionsDroped。在 绘制图表的指标 下 ,将统计数据更改为 总 和 , 将 周期 更改为 1 分钟 。你看到一条记录。如果您在几秒钟后没有看到指标,请刷新。

指标汇总视图
Lambda 停止递归循环时要采取的操作
当您收到有关账户递归的通知时,以下步骤可以帮助解决该问题。
-
要在修复底层配置问题时停止进一步的调用尝试,请将函数并发性设置为 0。这充当 Lambda 函数的关闭开关。你可以在
Lambda 控制台 中选择 “限制” 按钮, 也可以使用putFunctionConcurrency API 将函数并发 性设置为 0。 - 您也可以禁用或删除 Lambda 函数的事件源映射或触发器。
- 检查您的 Lambda 函数代码和配置中是否存在任何导致循环的代码缺陷。例如,检查您的环境变量以确保您使用的 SQS 队列或 SNS 主题与源和目标不相同。
-
如果 SQS 队列是您的 Lambda 函数的事件源,请在源队列 上配置
DLQ 。 -
如果 SNS 主题是事件源,请为 Lambda 函数
配置 “失败时 目的地 ”。
禁用递归检测
您可能有一些有效的用例,其中有意将 Lambda 递归作为设计的一部分。在这种情况下,请谨慎行事并设置适当的护栏,以防止对您的账户产生意外费用。要详细了解使用递归调用模式的最佳实践,请参阅 亚马逊云科技 Lambda 操作员指南
默认情况下,此功能处于启用状态以停止递归循环。要请求为您的账户将其关闭,请联系
结论
适用于 SQS 和 SNS 的 Lambda 递归控制会自动检测并停止在递归或无限循环中运行的函数。这可能是由于配置错误或编码错误造成的。递归控制有助于减少 Lambda 和下游服务的意外使用。这篇文章还解释了 Lambda 如何检测和停止递归循环,并通过 亚马逊云科技 Health Dashboard 通知您对函数进行故障排除。
要了解有关该功能的更多信息,请访问
如需更多无服务器学习资源,请访问
*前述特定亚马逊云科技生成式人工智能相关的服务仅在亚马逊云科技海外区域可用,亚马逊云科技中国仅为帮助您发展海外业务和/或了解行业前沿技术选择推荐该服务。